Schedule a free demo to learn more
6 Lesson Plan Formats Teachers Should Know: From Traditional to Blended Formats
29thOct 2025

Seven lesson plan formats to master include Traditional, 5E Inquiry, Backward Design, Differentiated, 3-Part Math, Multiple Intelligences and Flipped Learning.
Table of Contents: 6 Lesson Plan Formats
- Traditional / Direct Instruction Format
- 5E Inquiry Format
- Backward Design / Understanding by Design (UbD) Format
- Differentiated / Flexible Format
- Three-Part Lesson Format (Math Focus)
- Flipped / Blended Format
- Why knowing Multiple Formats expands breadth of knowledge
- Benefits of knowing Multiple Formats
- Quick Implementation Tips for Curriculum Leaders
- Frequently Asked Questions about Lesson Plan Formats and Curriculum Planning
- Maximizing Lesson Plan Formats for Effective Curriculum Planning
- Ready to Simplify Lesson Planning and Curriculum Mapping?
Modern K-12 education demands versatility. Teachers must meet standards, personalize instruction and nurture higher-order thinking; all this while managing time and accountability. The lesson plan format you choose shapes not only how you teach but also how students learn.
Whether you’re designing units in science, literacy or social studies, knowing multiple lesson plan formats gives you a flexible toolkit to reach all kinds of learners. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore six essential formats from traditional to flipped or blended ones. This will show you how each can align with effective curriculum mapping, curriculum management and curriculum planning for whole-school coherence.
Seven lesson plan formats to master include Traditional, 5E Inquiry, Backward Design, Differentiated, 3-Part Math and Flipped Learning. Each format strengthens your ability to plan with intention, align with curriculum frameworks and promote student engagement through diverse learning experiences that build a broader breadth of knowledge.
Let’s dive deeper into each of these lesson plan formats:
1. Traditional / Direct Instruction Format
The traditional lesson plan format remains the backbone of K-12 instruction. It’s structured, predictable, and ideal for introducing foundational skills or content. While some educators see it as ‘old-school’, its clarity and focus on measurable objectives still make it indispensable.
Why it works
In subjects like math, reading or grammar, explicit instruction ensures that students grasp essential procedures before moving into higher-order application. This model aligns neatly with backward planning as teachers start from the standard, craft clear objectives, then design guided and independent practice activities.
Structure example
- Objectives / Standards
- Materials / Resources
- Anticipatory Set (Hook)
- Direct Instruction / Modeling
- Guided Practice
- Independent Practice
- Closure / Reflection
- Assessment / Differentiation
Curriculum alignment
For curriculum mapping, traditional lessons can anchor benchmark skills across grade levels. A curriculum management system can then track where these core objectives appear, ensuring consistency across classrooms while allowing teachers to blend more exploratory formats elsewhere.
2. 5E Inquiry Format
(Engage – Explore – Explain – Elaborate – Evaluate)
The 5E model, widely used in science education, helps students learn through discovery and reflection. Instead of starting with explanation, students first experience a phenomenon and build conceptual understanding collaboratively.
Why it matters:
Inquiry-based learning cultivates curiosity, persistence, and deeper comprehension. For K-12 learners, especially in STEM subjects, the 5E sequence helps transition from teacher-led to student-driven learning while still maintaining structure.
Structure
- Engage: Introduce a problem, question, or demonstration to spark curiosity.
- Explore: Students investigate, test ideas or collaborate in hands-on tasks.
- Explain: Students articulate findings; the teacher formalizes key concepts.
- Elaborate: Apply learning to new contexts.
- Evaluate: Assess through discussion, performance or formal measures.
Connection to Curriculum Planning
Within curriculum mapping, 5E lessons can be placed at exploration phases in a unit sequence. This ensures that inquiry complements, rather than replaces, explicit instruction, achieving balance between depth and breadth of knowledge.
3. Backward Design / Understanding by Design (UbD) Format
Backward design reframes lesson planning as it begins with desired results, decides on assessment evidence, then design the learning experiences. This ‘end-in-mind’ framework, popularized by Wiggins & McTighe, ensures teaching always serves big conceptual goals.
Why is it a favorite among Curriculum Planners?
UbD fosters alignment between standards, assessment, and daily learning. It fits seamlessly within curriculum management systems, where outcomes and evidence drive lesson sequencing. Teachers can collaborate around shared ‘enduring understandings,’ improving instructional coherence across grades.
Structure
- Identify desired results (standards, essential questions)
- Determine acceptable evidence (performance tasks, tests, reflections)
- Plan learning experiences (instructional strategies, resources, scaffolds)
A Quick Implementation Guide:
- Focus on ‘transfer’, i.e. what knowledge or skill students should apply independently.
- Design performance tasks that reveal real understanding.
- During curriculum mapping, flag units with shared transfer goals to build vertical alignment.
This model helps schools avoid the pitfall of activity-driven teaching, keeping purpose front and center.
4. Differentiated / Flexible Format
No classroom is homogeneous. Differentiated lesson plans embrace that diversity through tailored goals, varied activities and flexible grouping. Students vary in readiness, interests and learning profiles. A differentiated approach allows teachers to address multiple pathways to the same outcome, ensuring equity without sacrificing rigor.
Structure
- Core Objective (common standard)
- Tiered Tasks or Choice Menus
- Flexible Grouping Plans
- Scaffolds and Extensions
- Formative Assessment Options
Planning integration Overview:
In curriculum planning, schools can build differentiation expectations directly into shared templates. For instance, a curriculum manager might note which units require high support or multiple modalities. Documenting these choices during curriculum mapping strengthens institutional memory and supports professional learning. Here’s a brief example:
When teaching persuasive writing, a teacher might offer:
- Analytical essay (linguistic intelligence)
- Speech or podcast (interpersonal/ verbal)
- Infographic (visual-spatial)
All meet the same standard but through student choice and varied expression.
5. Three-Part Lesson Format (Math Focus)
The three-part lesson model (Launch- Explore – Summarize) is common in math but useful across disciplines. Its goal is to move students from prior knowledge to deep understanding through problem-based exploration.
Why it works
Instead of over-scaffolding, students grapple with rich problems, share strategies and construct meaning collaboratively. It emphasizes conceptual reasoning and mathematical discourse, critical for long-term retention.
Structure
- Launch: Pose an engaging task or mental warm-up.
- Explore: Students work individually or in groups to solve problems.
- Summarize: Class discusses strategies and connects ideas to formal concepts.
From a Curriculum Perspective
During curriculum mapping, these lessons are perfect for mid-unit applications where exploration leads to consolidation. Over time, mapping multiple three-part lessons across grades ensures that mathematical reasoning, not just procedures, is taught systematically.
6. Flipped / Blended Format
Post-pandemic teaching has blurred classroom boundaries. Flipped or blended formats maximize face-to-face time for collaboration and feedback, while giving students flexibility and control over content pacing. In a flipped lesson, direct instruction happens outside of class, through videos, readings or digital tools; while class time is devoted to active practice, projects and individualized support.
Structure
- Pre-class: Students watch short videos or read material.
- In-Class: Discussion, application or lab-based work.
- Post-Class: Reflection or short assessment.
The Curriculum Planning Perspective
In curriculum mapping, mark which lessons are flipped to ensure even distribution and avoid overload. In curriculum management, digital tools like Edusfere’s platform can centralize pre-class materials and analytics, making flipped learning sustainable schoolwide.
Why knowing Multiple Formats expands breadth of knowledge
When teachers rely on one rigid template, they limit both engagement and cognitive growth. Rotating among lesson formats develops students’ breadth of knowledge , moving from recall to reasoning, creativity and synthesis.
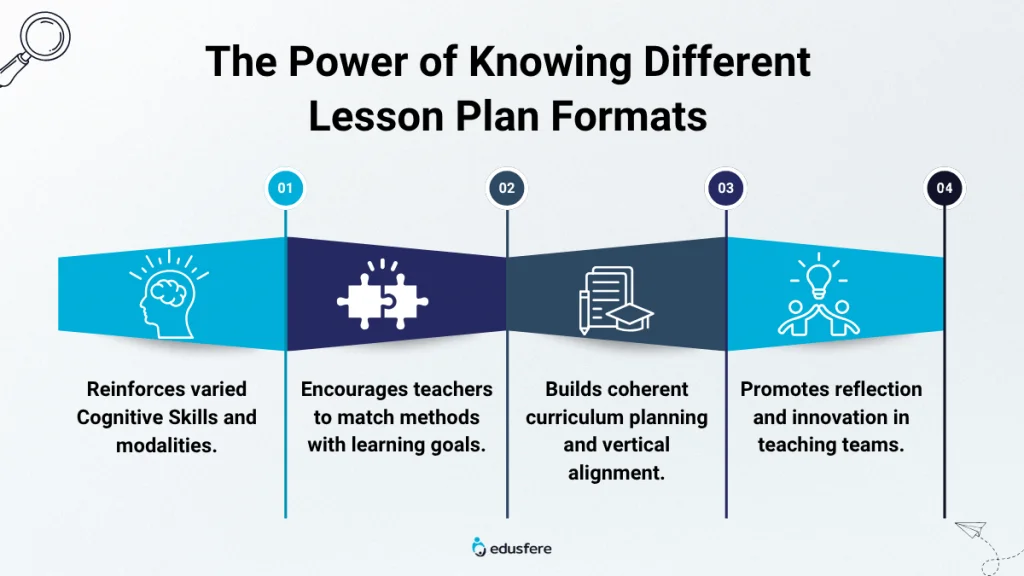
Benefits of knowing Multiple Formats
- Reinforces varied cognitive skills and modalities.
- Encourages teachers to match methods with learning goals.
- Strengthens coherence in curriculum planning and vertical alignment.
- Promotes reflection and innovation in teaching teams.
Schools that systematically integrate multiple lesson plan formats report higher engagement, stronger student agency and richer cross-disciplinary learning experiences.
Quick Implementation Tips for Curriculum Leaders
- Map lesson formats across the year. Ensure each format appears strategically in pacing guides.
- Use shared templates: Create consistent planning documents for each format so teachers can swap and adapt easily.
- Align professional development: Train teachers to identify which format best fits their objectives.
- Embed flexibility in curriculum management systems: Allow teachers to tag lesson formats, fostering variety without losing coherence.
- Collect and analyze data: Review which formats lead to higher student outcomes to inform ongoing planning cycles.
Frequently Asked Questions about Lesson Plan Formats and Curriculum Planning
Q1. What are the most common lesson plan formats used in K-12 classrooms?
The most common include Traditional, 5E Inquiry, Backward Design, Differentiated, Three-Part Math and Flipped formats- each addressing different teaching goals and learning styles.
Q2. What’s the difference between curriculum planning and curriculum mapping?
Curriculum planning focuses on designing learning experiences and aligning them to standards; curriculum mapping visually tracks when and where those standards are taught, ensuring vertical and horizontal alignment.
Q3. How can schools use curriculum management tools effectively?
Curriculum management platforms (like Edusfere) centralize lesson plans, pacing guides, and assessments, enabling collaboration, version control and data-informed improvement across departments.
Maximizing Lesson Plan Formats for Effective Curriculum Planning
Effective teaching is as much about how you plan as what you teach. By mastering these seven lesson plan formats, educators can move fluidly between structure and creativity, explicit instruction and inquiry, individual needs and collective goals.
Incorporating variety through intentional curriculum mapping and modern curriculum management tools ensures your lessons nurture not just mastery, but a true breadth of knowledge while preparing students for a world that values adaptability, collaboration and lifelong learning.
Ready to Simplify Lesson Planning and Curriculum Mapping?
At Edusfere, we help schools simplify and scale curriculum planning, mapping, and management while empowering teachers to design lessons that reflect real learner diversity. From direct instruction to multiple intelligences-based lessons, our platform brings coherence, flexibility and innovation into your instructional design process.
Ready to enrich your teachers’ repertoire and enhance your curriculum system?
Explore how Edusfere supports smarter lesson planning today.